RabbitMQ进阶 - RPC实现
RabbitMQMQ大约 3 分钟
RabbitMQ进阶 - RPC实现
1. 简介
Remote Procedure Call 简称 RPC,即远程调用。这个请自行百度。
这里 RPC 实现和传统的 RPC 还不太一样。
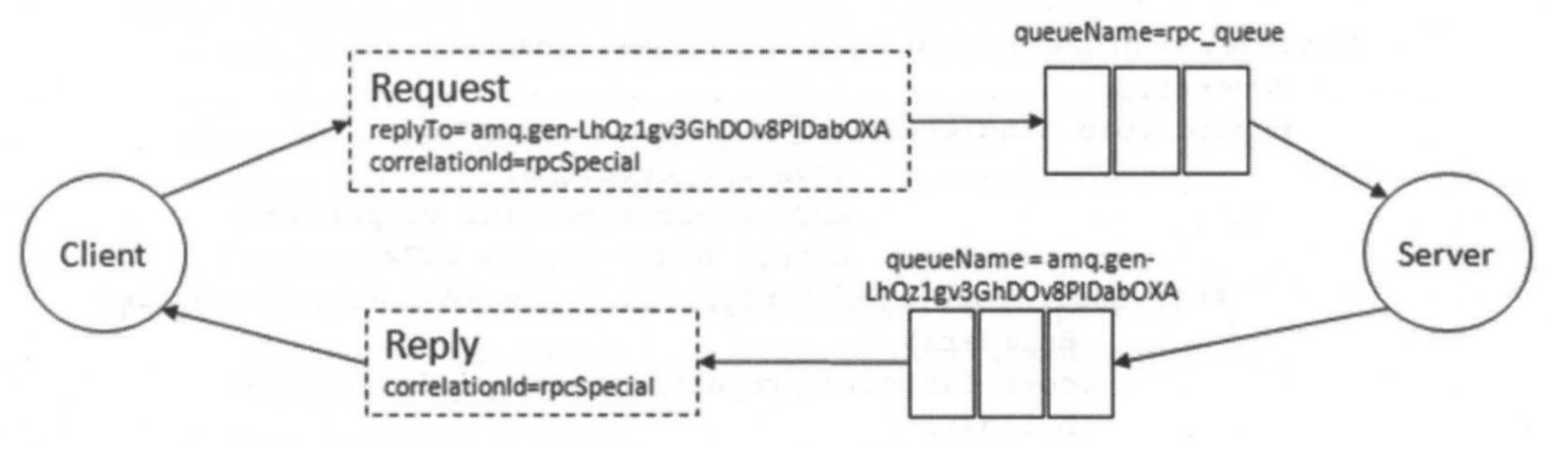
- 客户端发送一个请求,并设置了一个回复的队列
- 服务端,消费发送来的请求,并像这个回复的队列,响应了一个消息
2. 代码实现
就这个流程,通过消息队列来实现,
final AMQP.BasicProperties properties = new AMQP.BasicProperties()
.builder()
.correlationId(corrid)
.replyTo(replyQueue)
.build();
channel.basicPublish("", requestQueue, properties, "message".getBytes());
可以通过发送消息时指定 replyTo 和 correlationId 属性:
replyTo :通常用来设置一个回调队列
correlationId :用来关联请求(request)
为每个 RPC 请求创建一个回调队列,效率很低,可以使用这个通用的解决方案:为每个客户端创建一个单一的回调队列。
多个 RPC 共用一个回调队列,就存在哪一个请求对应的响应是什么?那么这个 correlationId 就是解决这个问题的。
核心思路就是利用这两个属性,来模拟 RPC 的实现。下面是一个例子,尽管这个例子模仿了 RPC 的调用,但是存在一个问题,不能在多线程中调用。所以该例子是一个半成品。
2.1 详细例子
RpcServer 服务端
package cn.mrcode.rabbitmq.rpc;
import com.rabbitmq.client.AMQP;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
import com.rabbitmq.client.ConnectionFactory;
import com.rabbitmq.client.DefaultConsumer;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Envelope;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeoutException;
public class RpcServer {
private static String rpcQueue = "rpc_queue";
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {
final String IP_ADDRESS = "192.168.4.250";
final int PORT = 5672;
final ConnectionFactory factory = new ConnectionFactory();
factory.setHost(IP_ADDRESS);
factory.setPort(PORT);
factory.setUsername("admin");
factory.setPassword("root");
final Connection connection = factory.newConnection();
final Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
channel.queueDeclare(rpcQueue, false, false, false, null);
channel.basicQos(1);
System.out.println(" [x] Awaiting RPC requests");
channel.basicConsume(rpcQueue, false, new DefaultConsumer(channel) {
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
// 正常的消费消息
final String message = new String(body, "UTF-8");
System.out.println(" [.] message: " + message);
// 然后再发出去一条消息
final AMQP.BasicProperties replyProps = new AMQP.BasicProperties().builder()
.correlationId(properties.getCorrelationId())
.build();
channel.basicPublish("", properties.getReplyTo(), replyProps, (message + " reply").getBytes());
channel.basicAck(envelope.getDeliveryTag(), false);
}
});
}
}
RpcClient 客户端
package cn.mrcode.rabbitmq.rpc;
import com.rabbitmq.client.AMQP;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Address;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
import com.rabbitmq.client.ConnectionFactory;
import com.rabbitmq.client.QueueingConsumer;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.UUID;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeoutException;
public class RpcClient {
final String IP_ADDRESS = "192.168.4.250";
final int PORT = 5672;
final Address[] addresses = {
new Address(IP_ADDRESS, PORT)
};
private Connection connection;
private Channel channel;
// 请求服务端的队列名
private String requestQueue = "rpc_queue";
// 服务器处理完成后,响应的队列名称
private String replyQueue;
// 等待回调
private QueueingConsumer queueingConsumer;
public RpcClient() throws IOException, TimeoutException {
final ConnectionFactory factory = new ConnectionFactory();
factory.setUsername("admin");
factory.setPassword("root");
connection = factory.newConnection(addresses);
channel = connection.createChannel();
// 生命的响应队列:是一个临时的队列
replyQueue = channel.queueDeclare().getQueue();
queueingConsumer = new QueueingConsumer(channel);
channel.basicConsume(replyQueue, true, queueingConsumer);
}
public String call(String message) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
final String corrid = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
final AMQP.BasicProperties properties = new AMQP.BasicProperties()
.builder()
.correlationId(corrid)
.replyTo(replyQueue)
.build();
channel.basicPublish("", requestQueue, properties, "message".getBytes());
// 想服务端发送后,轮询,知道回去到服务端的响应为止
while (true) {
final QueueingConsumer.Delivery delivery = queueingConsumer.nextDelivery();
if (delivery.getProperties().getCorrelationId().equals(corrid)) {
return new String(delivery.getBody());
}
}
}
private void close() throws IOException {
connection.close();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException, InterruptedException {
// 客户端调用
final RpcClient rpcClient = new RpcClient();
System.out.println(" [x] Requesting call(30)");
final String response = rpcClient.call("30");
System.out.println(" [.] Got '" + response + "'");
rpcClient.close();
}
}
运行这个程序,服务端和客户端的输出如下
# 服务端
[x] Awaiting RPC requests
[.] message: message
# 客户端
[x] Requesting call(30)
[.] Got 'message reply'
从客户端调用来看,非常像我们在调用一个 service。 这就是用队列模拟了 RPC 调用。
客户端和服务端发送都没有定义交换器,是空串,这个应该是 RabbitMQ 默认的交换器?
这里笔者需要强调一点的是:以上类,使用了临时队列之类的声明,不要被这个迷惑了。他的核心思路就是:
客户端发送消息到一个 **队列 A ** 中
发送消息时,通过参数传递
replyTo和correlationId服务端消费 **队列 A ** 中的消息
并处理这个消息,然后从参数中拿到
correlationId作为参数,把处理结果发送给从参数中获得的回调队列replyTo客户端接受响应消息
只是在语法上将异步调用模拟成了同步调用
参考文章
Loading...